Nissan Altima (L32) 2007-2012 Service Manual: Diagnosis and repair workflow
Work Flow
INTRODUCTION
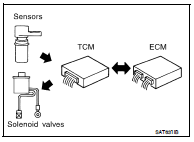
The TCM receives a signal from the vehicle speed sensor, PNP switch and provides shift control or lock-up control via CVT solenoid valves.
The TCM also communicates with the ECM by means of a signal sent from sensing elements used with the OBD-related parts of the CVT system for malfunction-diagnostic purposes. The TCM is capable of diagnosing malfunctioning parts while the ECM can store malfunctions in its memory.
Input and output signals must always be correct and stable in the operation of the CVT system. The CVT system must be in good operating condition and be free of valve seizure, solenoid valve malfunction, etc.
It is much more difficult to diagnose an error that occurs intermittently rather than continuously. Most intermittent errors are caused by poor electric connections or improper wiring. In this case, careful checking of suspected circuits may help prevent the replacement of good parts.
A visual check only may not find the cause of the errors. A road test with CONSULT-III (or GST) or a circuit tester connected should be performed. Follow the “DETAILED FLOW”.

Before undertaking actual checks, take a few minutes to talk with a customer who approaches with a driveability complaint. The customer can supply good information about such errors, especially intermittent ones. Find out what symptoms are present and under what conditions they occur. A “Diagnostic Work Sheet” as shown on the example (Refer to TM-86) should be used.
Start your diagnosis by looking for “conventional” errors first. This will help troubleshoot driveability errors on an electronically controlled engine vehicle.
Also check related Service bulletins.

DETAILED FLOW
1.COLLECT THE INFORMATION FROM THE CUSTOMER
Get the detailed information from the customer about the symptom (the condition and the environment when the incident/malfunction occurred) using diagnosis worksheet. Refer to TM-86, "Diagnostic Work Sheet".
>> GO TO 2.
2.CHECK SYMPTOM 1
Check the following items based on the information obtained from the customer.
• Fail-safe. Refer to TM-219, "Fail-safe".
• CVT fluid inspection. Refer to TM-240, "Inspection".
• Line pressure test. Refer to TM-247, "Inspection and Judgment".
• Stall test. Refer to TM-245, "Inspection and Judgment".
>> GO TO 3.
3.CHECK DTC
1. Check DTC.
2. Perform the following procedure if DTC is detected.
• Record DTC.
• Erase DTC. Refer to TM-117, "Diagnosis Description".
Is any DTC detected? YES >> GO TO 4.
NO >> GO TO 6.
4.PERFORM DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE
Perform “Diagnostic Procedure” for the displayed DTC.
>> GO TO 5.
5.PERFORM DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
Perform “DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE” for the displayed DTC.
Is DTC detected? YES >> GO TO 4.
NO >> GO TO 6.
6.CHECK SYMPTOM 2
Try to confirm the symptom described by the customer.
Is any malfunction present? YES >> GO TO 7.
NO >> INSPECTION END
7.RODE TEST
1. Perform “RODE TEST”. Refer to TM-249, "Description".
>> GO TO 8.
8.CHECK SYMPTOM 3
Try to confirm the symptom described by the customer.
Is any malfunction present? YES >> GO TO 2.
NO >> INSPECTION END
Diagnostic Work Sheet
INFORMATION FROM CUSTOMER
KEY POINTS
• WHAT..... Vehicle & CVT model
• WHEN..... Date, Frequencies
• WHERE..... Road conditions
• HOW..... Operating conditions, Symptoms


DIAGNOSTIC WORK SHEET


 Basic inspection
Basic inspection Inspection and adjustment
Inspection and adjustment